THE WHY AND HOW OF LANDING ROCKETS
Some of you may have been following our recent attempts to vertically land the first stage of our Falcon 9 rocket back on Earth.
There was this attempt in January, followed by this one in April.

These landing attempts move us toward our goal of producing a fully and rapidly reusable rocket system, which will dramatically reduce the cost of space transport.
A jumbo jet costs about the same as one of our Falcon 9 rockets, but airlines don’t junk a plane after a one-way trip from LA to New York. Yet when it comes to space travel, rockets fly only once—even though the rocket itself represents the majority of launch cost.
The Space Shuttle was technically reusable, but its giant fuel tank was discarded after each launch, and its side boosters parachuted into corrosive salt water every flight, beginning a long and involved process of retrieval and reprocessing. So, what if we could mitigate those factors by landing rockets gently and precisely on land? Refurbishment time and cost would be dramatically reduced.
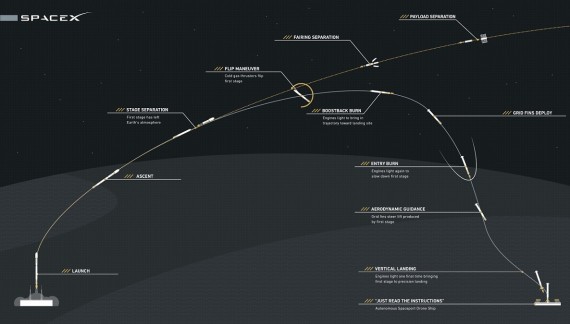
Historically, most rockets have needed to use all of their available fuel in order to get their payload into space. SpaceX rockets were built from the beginning with reusability in mind—they have enough built-in fuel margin to deliver a Dragon to the space station and return the first-stage to Earth. That extra fuel is needed to reignite the engines a few times to slow the rocket down and ultimately land the first stage after it has sent the spacecraft on its way.
In addition to extra fuel, we’ve added a few critical features to our Falcon 9 first stage for reusability’s sake. Our rocket has small, foldable heat-resistant wings called grid fins needed for steering the first-stage as it plummets from the edge of space through Earth’s atmosphere, cold-gas thrusters on the top of the first-stage that are used to flip the rocket around as it begins its journey back to Earth, and strong but lightweight carbon fiber landing legs that deploy as it approaches touchdown. All of these systems, while built and programmed by humans, are totally automated once the rocket is launched—and are reacting and adjusting their behavior based on incoming, real-time data.
So, what have we learned from the most recent landing attempts?
The first attempt to land on a drone ship in the Atlantic was in January, and while we came close, the first stage prematurely ran out of the hydraulic fluid that is used to steer the small fins that help control the rocket’s descent. The vehicle has now been equipped with much more of that critical fluid for steering purposes.
Our second attempt was in April, and we came close to sticking this landing. Check out this previously unreleased, longer video from our tracking camera. It shows the stage’s descent through the atmosphere, when the vehicle is traveling faster than the speed of sound, all the way to touchdown.
Last-second tilt aside, the landing attempt happened pretty much exactly as planned. Shortly after stage separation (when the second stage leaves the first stage behind and goes on to carry Dragon to orbit), cold gas thrusters fired to flip the stage to reorient it for reentry. Then, three engines lit for a “boostback burn” that slows the rocket and brings it toward the landing site.
The engines then re-lit to slow the stage for reentry through Earth’s atmosphere, and grid fins (this time with much more hydraulic fluid) extended to steer the lift produced by the stage. Our atmosphere is like molasses to an object traveling at Mach 4, and the grid fins are essential for landing with precision. The final landing burn ignited, and together the grid fins, cold gas thrusters and steerable engines controlled the vehicle, keeping the stage within 15 meters of its target trajectory throughout the landing burn. The vehicle’s legs deployed just before it reached our drone ship, “Just Read the Instructions”, where the stage landed within 10 meters of the target, albeit a bit too hard to stay upright.
Post-launch analysis has confirmed the throttle valve as the sole cause of this hard landing. The team has made changes to help prevent, and be able to rapidly recover from, similar issues for the next attempt, which will be on our next launch—the eighth Falcon 9 and Dragon cargo mission to the space station, currently scheduled for this Sunday.
Even given everything we’ve learned, the odds of succeeding on our third attempt to land on a drone ship (a new one named “Of Course I Still Love You”) are uncertain, but tune in here this Sunday as we try to get one step closer toward a fully and rapidly reusable rocket.
Read My Profile










Recent Comments